BLOCKCHAIN 101
What is Blockchain?
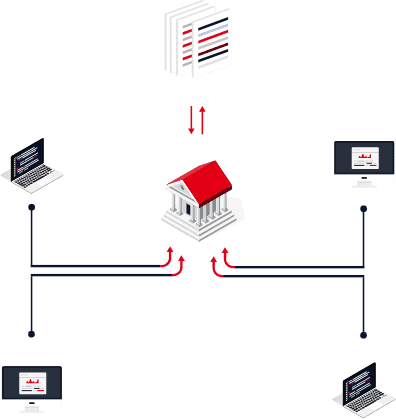
Blockchain technology enables everyone involved in a transaction to know with certainty what happened, when it happened, and confirm other parties are seeing the same thing without the need for an intermediary providing assurance, and without a need to reconcile data afterwards.
The two terms “blockchain” and “DLT” are often used interchangeably and to understand blockchain, it’s important to understand Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) — the framework that underpins it.

What is Distributed Ledger Technology?
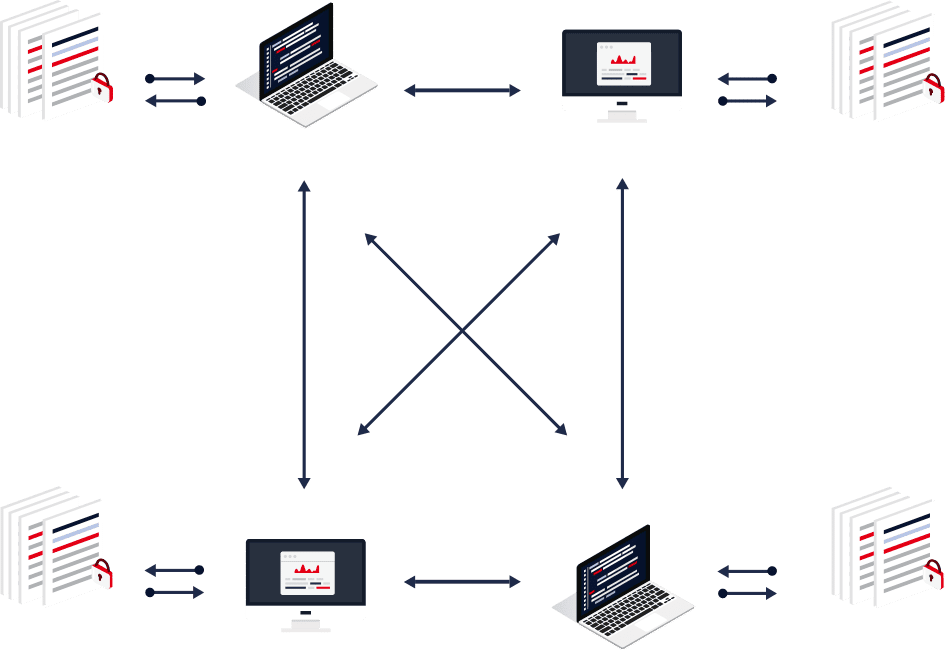
DLT is a decentralized database managed by multiple participants, across multiple nodes. Blockchain is a type of DLT where transactions are recorded with an immutable cryptographic signature called a hash. The transactions are then grouped in blocks and each new block includes a hash of the previous one, chaining them together, hence why distributed ledgers are often called blockchains.

Is Corda a blockchain?
Corda is both a blockchain and not a blockchain.
Transactions on Corda are cryptographically linked or chained to the transactions it depends upon. So, by definition, Corda is a blockchain—with one key differentiator.
Corda does not periodically batch up transactions needing confirmation — into a block — and confirm them in one go. Instead, Corda confirms each transaction in real-time. With Corda, there is no need to wait for other transactions to come along or a “block interval”. Transactions are confirmed immediately. This means that your transaction is not dependent on any others, increasing both privacy and scalability.